What is Aspartame?

What is Aspartame?
Aspartame is a high-intensity sweetener made from amino acids. Aspartame is considered safe and is approved for consumption in more than 125 countries and territories worldwide.
Table of contents
Aspartame, a safe sweetener, is made from amino acids, the building blocks of protein
Each amino acid has its own unique taste. Amino acids can be combined to produce new flavors and functions.
Aspartic acid has a sour taste with a hint of umami, while phenylalanine has a bitter taste. Aspartame is made by binding these two amino acids to produce a high-intensity sweetener that is 200 times sweeter than sugar. It does not impact blood sugar levels.
Aspartame is made from amino acids— the same amino acids that make up proteins in the foods we consume every day, such as meats, dairy products, grains and vegetables. In the body, aspartame is broken down into amino acids, making it safe to consume.
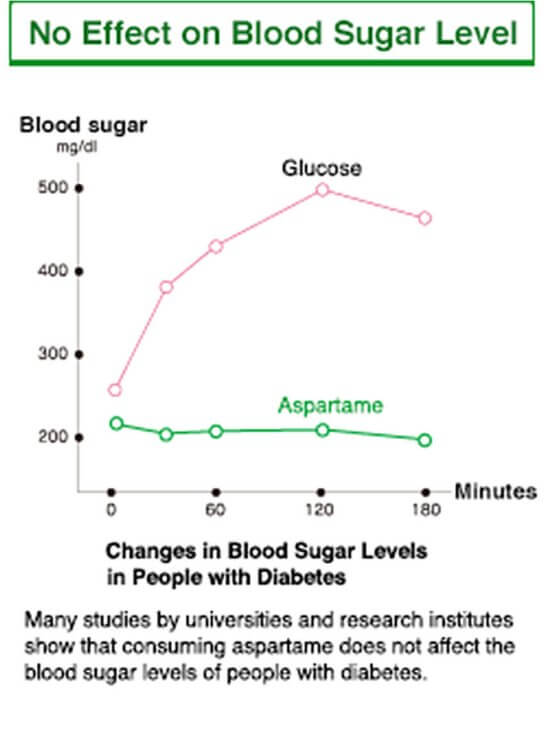
No Effect on Blood Sugar Level
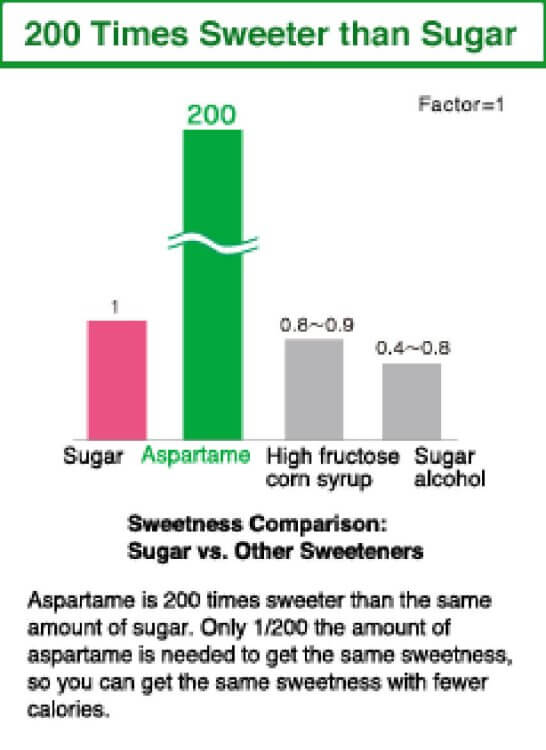
200 Times Sweeter than Sugar
A Natural Sweetness Like Sugar
Aspartame has a sweetness profile similar to sugar. Unlike other high-intensity sweeteners, aspartame has no peculiar aftertaste or bitterness—just a natural sweetness that enhances the flavor of foods.
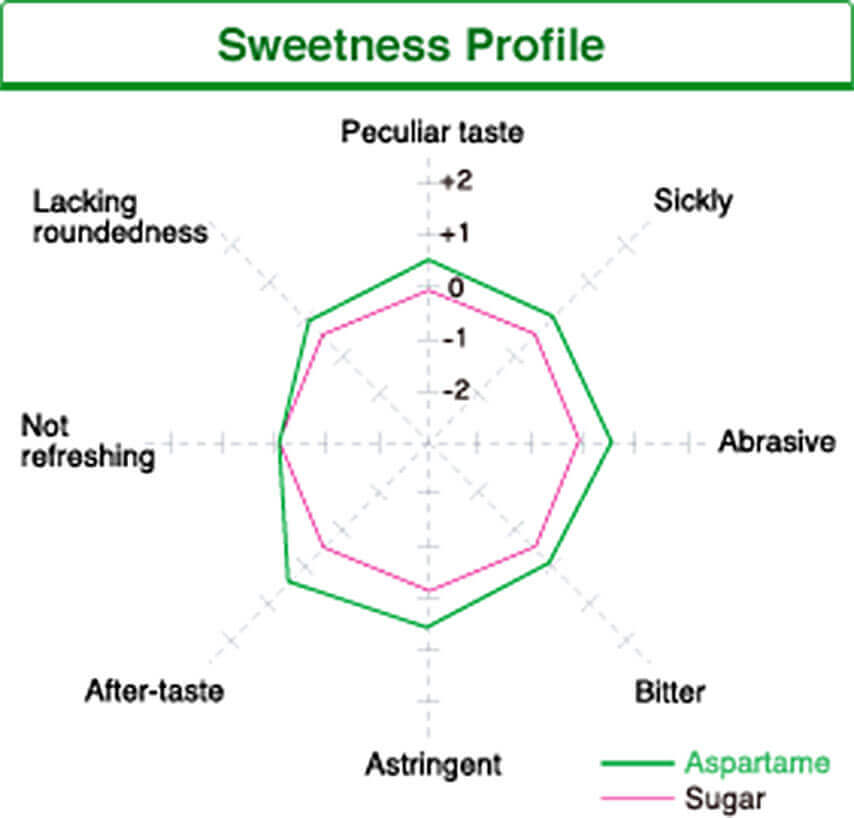
Sweetness Profile
Aspartame—Approved in Over 125 Countries and
Territories Worldwide
The safety of aspartame has been repeatedly demonstrated through research and testing. These tests show that aspartame is safe to consume.
Aspartame has been approved as safe to consume in over 125 countries and territories worldwide. This includes the United States, Europe, Asia, and Africa. The Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA)1, an international body, has set the acceptable daily intake (ADI)2 of aspartame at 40 milligrams per kilogram of body weight. In 1983, the Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare (now the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare) approved aspartame as a food additive after a thorough review by its Food Sanitation Council.
1The Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) is administered by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
2Acceptable daily intake (ADI) is the maximum amount of a given food additive a person can ingest daily over a lifetime without negative health effects.
Aspartame FAQs
What amino acids are used to make aspartame? How is aspartame made?
Aspartame is an amino acid-based sweetener that is 200 times sweeter than sugar. Aspartame is made from the amino acids aspartic acid and phenylalanine, which are found in many foods and proteins. Aspartame is made by forming peptide bonds of aspartic acid and phenylalanine. It is then refined and dried. These peptide bonds are also formed when amino acids are made into proteins. The amino acids in aspartame are digested, absorbed, metabolized, and excreted just like the amino acids in regular foods.
Is aspartame considered to be safe?
Following comprehensive reviews of the medical literature, aspartame has been deemed safe by JECFA, the United States FDA, and the Food Sanitation Council of Japan.
According to the FDA, “Aspartame is one of the most exhaustively studied substances in the human food supply.”
(http://www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/FoodAdditivesIngredients/ucm397725.htm)
Furthermore, a 2002 review by the the European Union’s Scientific Committee on Food (SCF) declared, “Aspartame is unique among the intense sweeteners in that the intake of its component parts can be compared with intakes of the same substances from natural foods.”
(https://ec.europa.eu/food/sites/food/files/safety/docs/sci-com_scf_out155_en.pdf)
Aspartame is currently approved for consumption in over 125 countries and territories worldwide, including in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and France.
Can aspartame be safely consumed every day?
It is considered safe to consume aspartame daily in moderate amounts. If you were to replace sugar in your diet with relatively the same amount of aspartame based on sweetness, you would on average consume just 1/5 the acceptable daily intake (ADI) in the United States, 2/7 the ADI in the European Union, and 1/6 the ADI in Japan.*
*Calculation based on a body weight of 50 kilograms (110 pounds).
Does aspartame affect blood sugar levels? Will I lose weight if I switch from sugar to aspartame?
Aspartame is digested, absorbed, metabolized, and excreted in the body as amino acids. It has no effect on blood sugar levels. Aspartame is different from sugar and is used only in small amounts, so it doesn’t stimulate the secretion of insulin.
Consuming aspartame can reduce your overall calorie intake. However, switching from sugar to aspartame by itself will not make you lose weight.
Is it safe to consume aspartame while pregnant or breastfeeding? Will extended consumption of aspartame affect a child's growth?
Aspartame is digested, absorbed, metabolized, and excreted in the body in the same way as amino acids are in regular foods. Women can safely consume aspartame while pregnant or breastfeeding.
Studies show no effect on the fetus even when three times the acceptable daily intake (ADI) of aspartame is consumed. Studies have also shown that aspartame is safe for children to consume regularly.
Content you may like

How Amino Acids Can Solve the World’s Health and Nutrition Challenges
These days we hear a lot about amino acids. But many of us probably don’t understand how they work or their link to human health. ...

Amino Acid Supplementation for Working Out
If used in the right way, amino acids supplementation can help with muscle conditioning and recovery, boost endurance, and build muscle mass more efficiently.Table of ...

Amino Acids for Healthy Aging
Leveraging amino acids to extend healthy life expectancy Amino acids are important for addressing loss of muscle mass as we ageAs we get older, we ...
