A liquid-phase
synthesis technology

AJIPHASE®
Kokumi delivers background richness, roundness and complexity to savory products such as a stew simmered for several hours. They hold great potential for delivering more of what we want and reducing what we don’t need, without sacrificing flavor.
< Table of Contents >
-
Developing therapeutics that treat diseases better -
The Path to Development—applying amino acid technology to pharmaceutical manufacturing -
The “Anchor” Breakthrough—combining the merits of both solid-phase and liquid-phase syntheses -
Moving to the Next Phase—the challenge of manufacturing oligonucleotide-based drug therapies

Developing therapeutics
that treat diseases better
Human beings have long depended on medicine to cure diseases. But new drug discoveries have a long road to travel before reaching patients, from research and development to clinical trials, regulatory approval, and commercialization. To develop drugs more seamlessly, it is common for pharmaceutical companies to outsource drug manufacturing to third parties.
But if the manufacturing process is altered between clinical testing and commercialization, time must be spent to re-evaluate a drug’s safety, with a risk of delaying drug development. The Ajinomoto Group solves this problem with a revolutionary new manufacturing method called AJIPHASE®. This unique technology makes it feasible to scale up from small-scale synthesis for R&D to large-scale synthesis for mass production.
The Ajinomoto Group’s AJIPHASE® technology is helping innovative medicines reach as many patients as possible by ensuring stable production. AJIPHASE® is a liquid-phase synthesis technology augmented by certain proprietary improvements developed by Ajinomoto Co., Inc. This technology makes it possible to produce high-quality compounds with high scalability.
The Path to Development—applying amino acid
technology to pharmaceutical manufacturing
The Ajinomoto Group has more than a century’s worth of research and development in the field of amino acid technology. It all began in 1908, when Dr. Kikunae Ikeda of Tokyo Imperial University (now the University of Tokyo) isolated crystals that conveyed the taste he had detected. These crystals were made of glutamate—one of the most common amino acids in foods, and in the human body. Thus, the umami seasoning AJI-NO-MOTO® was born. Since then, the Ajinomoto Group has developed a wide variety of businesses by leveraging our ongoing research into the properties and functions of amino acids.
In the late 1980s, the Ajinomoto Group began manufacturing drug therapies developed by pharmaceutical companies. During the 1990s, we contributed to the production of drugs used in the treatment of AIDS, herpes simplex and hypertension. Since 2005, the Ajinomoto Group had sought to apply our amino acid technology to the synthesis of peptides, chains of multiple amino acids that are a common component of many pharmaceuticals. This has come to fruition in the development of a practical manufacturing process for peptides—AJIPHASE®.
The “Anchor” Breakthrough—combining the merits
of both solid-phase and liquid-phase syntheses
Solid-phase synthesis has been the major manufacturing process for synthesizing oligonucleotides and peptides. In solid-phase synthesis the reaction proceeds in a column charged with a solid support through which the reagents and solvents are flowed. One elongation typically requires several reactions, with a solvent wash for each step, to remove the remaining reagents from the column. Although this process has been fully automated and is rapid, the consumption of reagents and solvents is generally higher than that of liquid-phase synthesis. Given several other limitations and drawbacks, solid-phase synthesis is known to have limited scalability, with only up to kilogram-scale synthesis having been achieved.
Contrary to solid-phase synthesis, AJIPHASE® technology uses an anchor support that is soluble in the organic solvent in which the reactions take place. This provides a uniform distribution of reagents in the system, and thus results in a higher homogeneity and efficiency of the reactions compared to solid-phase synthesis. Therefore, unlike solid-phase synthesis, the consumption of excess reagents can be decreased with AJIPHASE® technology. In addition, the manufacturing of peptides and oligonucleotides via AJIPHASE® can be performed in a conventional batch reactor, which also obviates the need for special equipment for automated controls required in solid-phase synthesis.
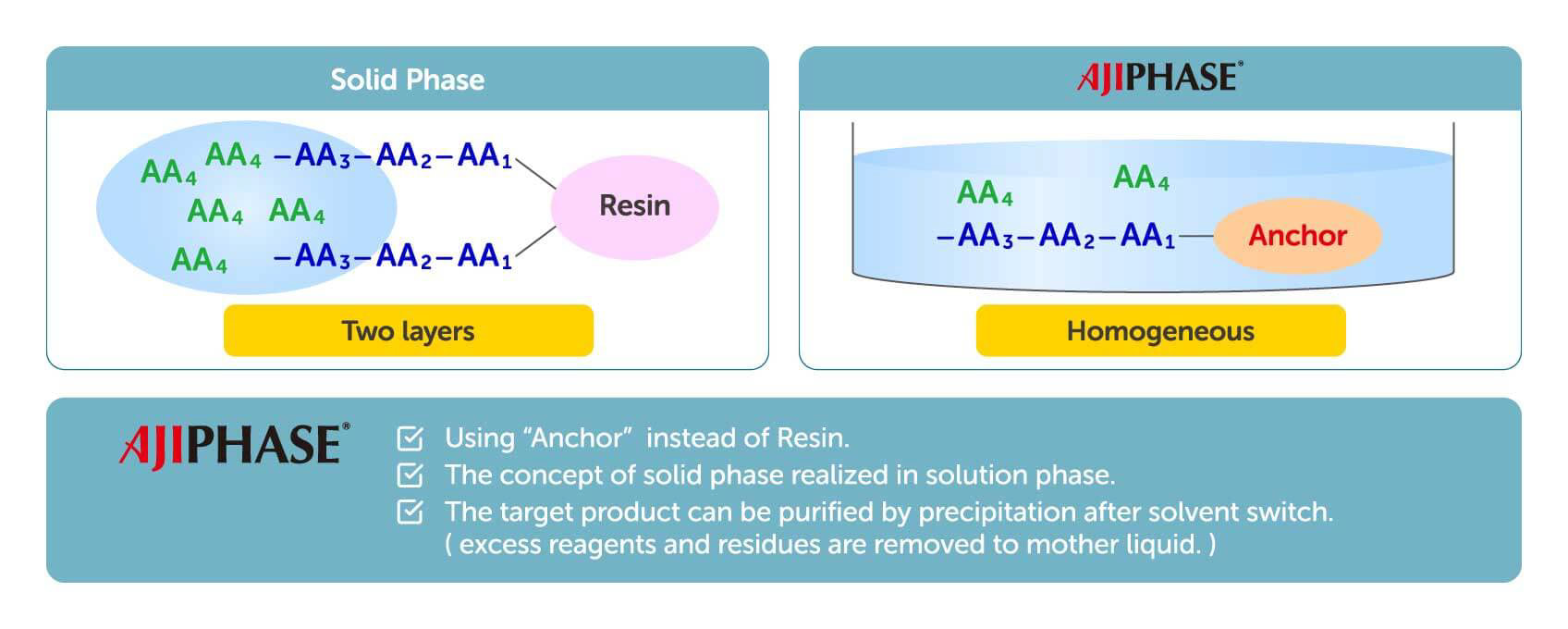
Combining the merits of both solid-phase synthesis and liquid-phase synthesis has provided a breakthrough in our manufacturing strategy. Crucially, the discovery of anchor supports that dissolve in a specific organic solvent but not in others provided a powerful alternative to the insoluble resin beads used in solid-phase synthesis. The target crude can be easily precipitated in a batch reactor by adding insoluble solvent. The precipitates can then be obtained by filtration, and a simple wash with poor solvents can eliminate all reagents used in reactions. This easy workup has largely contributed to our development of a robust and practical manufacturing method for peptides and oligonucleotides.
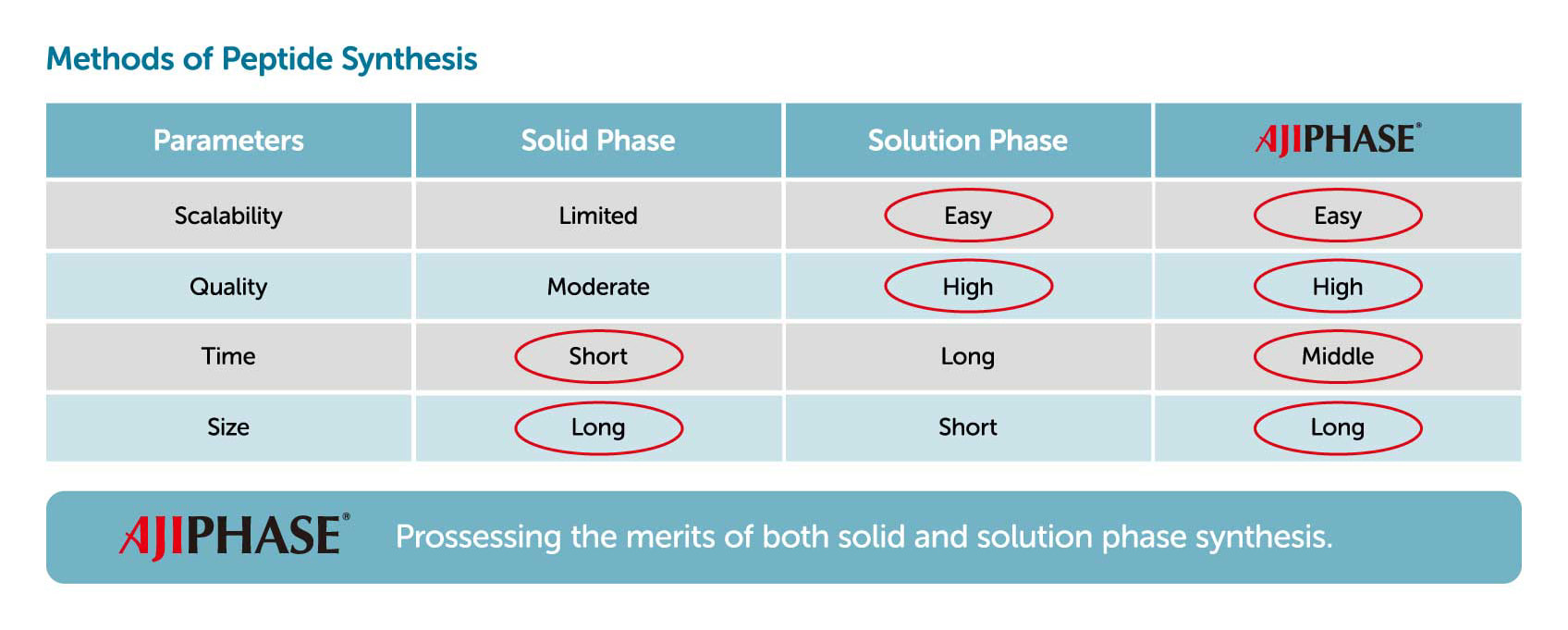
Moreover, AJIPHASE® makes it possible to perform process analysis directly during the synthesis of the target compound, enabling timely processing. Through stringent process control, the manufacture of active pharmaceutical ingredients, or APIs, can be performed on the order of several tens of kilograms at a time while still ensuring high quality. Being able to synthesize very small to very large quantities of API ensures drug companies a stable supply. And because the amount of solvent used is significantly reduced compared to the solid-phase synthesis method, AJIPHASE® is also environmentally friendly.
Moving to the Next Phase—the challenge of
manufacturing oligonucleotide-based drug therapies
Moving to the Next
Phase—the challenge of
manufacturing
oligonucleotide-based
drug therapies
Not all medicines function the same way. Drug therapies come in different types. In recent years, oligonucleotide therapeutics have been attracting attention as a new drug platform. Effective in some cases even with diseases where other drugs have been ineffective, oligonucleotide therapeutics are raising expectations in the pharmaceutical and medicinal fields. For example, it is hoped that oligonucleotide therapeutics could prove effective against congenital muscular dystrophy.
Proteins consist of chains of peptides that contain up to twenty different amino acids. Our bodies produce proteins to build strong muscles. But in patients with muscular dystrophy, a genetic mutation disables production of dystrophin proteins required for muscles to function. Defective dystrophin production results in muscle weakness, making it difficult for individuals with this intractable condition to walk. Muscle weakness begins in childhood, leading to loss of motor skills, and, in extreme cases, problems with breathing, swallowing, or even blood circulation.
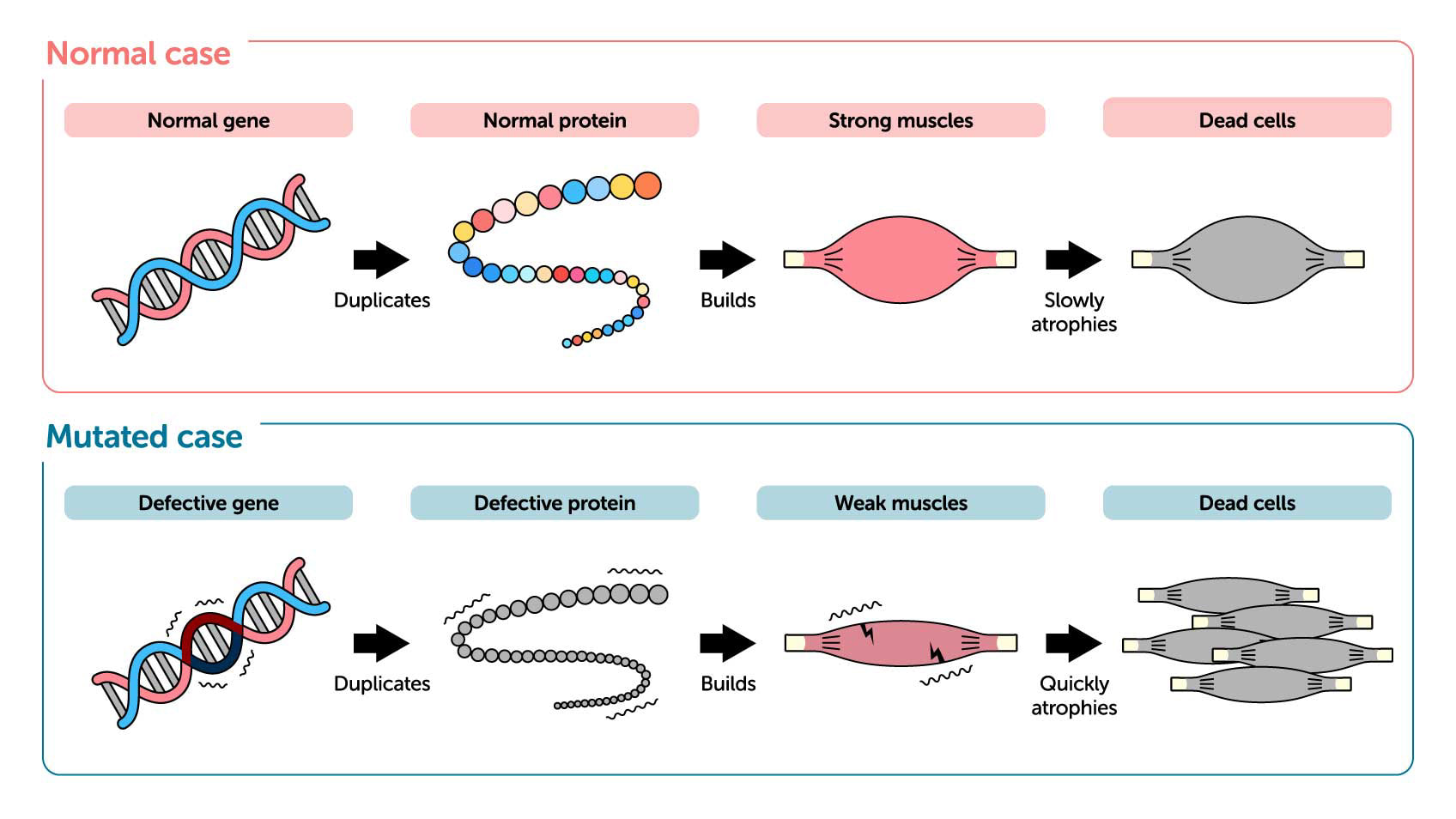
Until now, treatments have included small-molecule drugs used to suppress cell necrosis—or the death of muscle cells—with adrenal steroids. Another is anti-myostatin therapeutics that inhibit the action of the protein myostatin, which suppresses muscle development, in order to maintain adequate muscle mass and promote muscle development. However, neither treatment has proven comprehensive. Oligonucleotide therapeutics, on the other hand, make use of these substances’ unique ability to control the genetic information encoded in our RNA and to inhibit the function of target protein. In the case of congenital muscular dystrophy, they make it possible to skip mutated muscle genes during protein replication in order to encourage the production of functional proteins.
Starting in 2011, we began to apply our AJIPHASE® technology to the manufacturing of morpholinos, one of the artificial oligonucleotides, as this process is chemically similar to the method that we developed for manufacturing peptides. In 2015, we launched a new phase for the technological development of oligonucleotides, as the next drug modality for our AJIPHASE® technology. In 2020, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved the first drug manufactured using AJIPHASE® process.

With several approvals of oligonucleotide therapeutics for the treatment of muscular atrophy and dystrophy over the past decade, oligonucleotide therapeutics now hold the potential to have a remarkable effect on the treatment of neurological disorders as well as other conditions. In addition, it is expected that oligonucleotides have the potential to enhance the efficacy of vaccines for diseases such as COVID-19. Research aimed at expanding the range of target tissues and organs holds great promise for future growth in the nucleic acid pharmaceutical industry.
The Ajinomoto Group is deeply committed to contributing to the health of people around the world by unlocking the power of amino acids. In order to deliver oligonucleotide and other cutting-edge therapies to pharmaceutical companies, we are tirelessly continuing our research not only to advance AJIPHASE® technology, but also to provide the best technology for drug providers and patients alike.
For more info about AJIPHASE🄬:
- AJIPHASE® | Ajinomoto Bio-Pharma Services Platform Technologies
- AJIPHASE Synthesis | Ajinomoto Bio-Pharma Services
Related Video
What is AJIPHASE®?

Another Innovation Story